What Is Bamboo Fabric and How it's Made?
Bamboo fabric comes from the fibers of the bamboo plant which is soft, breathable, and eco-friendly. Eco-friendly bamboo pulp is processed into fibers that can be spun and woven into fabric like any other textile. While often compared to cotton, bamboo fabric is softer, stretchier, thinner, yet just as strong and durable.

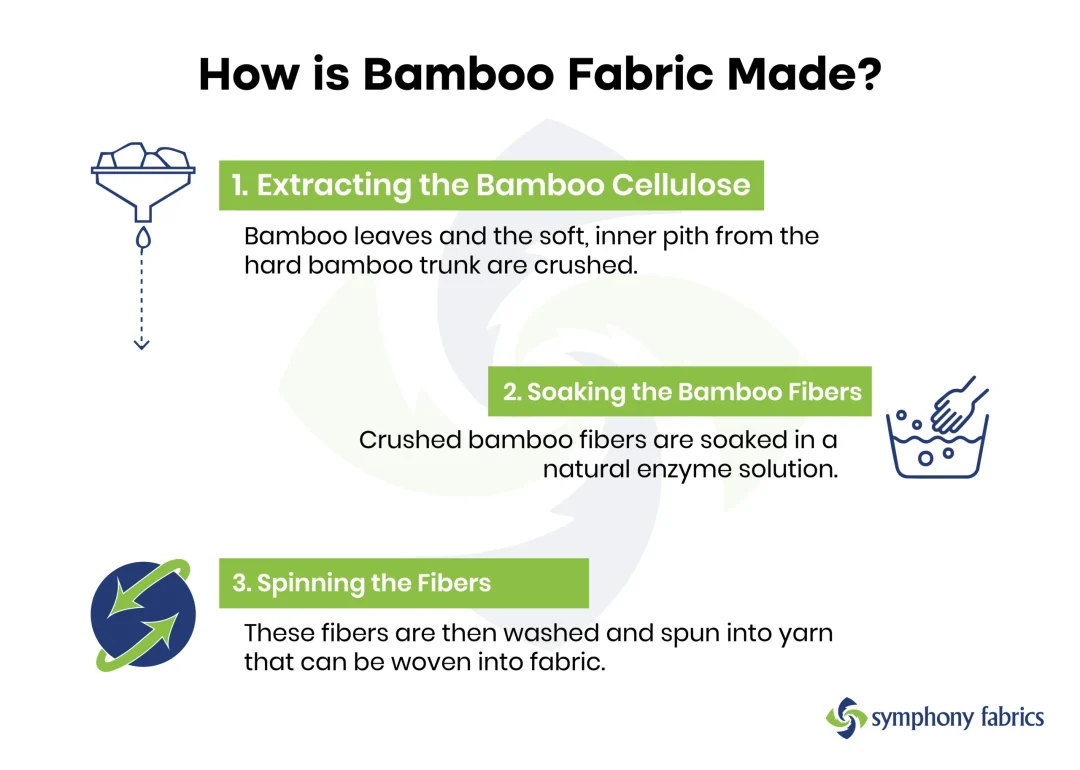
There are two methods to convert bamboo into fabric The mechanical process and the chemical process each of which has distinct characteristics.
Mechanical Process (Natural Enzyme Treatment).
Mechanical method is the greener option however it is not widely used because of its labour-intensive nature and high cost.
- Harvesting and Crushing Bamboo stalks that are mature are collected and then broken to smaller bits.
- Enzyme Treatment Natural enzymes are used to break down bamboo’s woody structure, and then to separate the fibers.
- “Film Extraction”: fibers that have softened are then combed and made into a yarn.
- Fabric Production Fabric Production: The yarn is spun into a fabric with the same texture as linen.
How it’s Made?
This method avoids harsh chemicals and produces a fabric that is biodegradable and sustainable. However, due to its complexity and cost, it is not widely adopted in large-scale manufacturing.
- Chemical Process (Viscose Method)
The majority of bamboo fabric on the market is produced using the viscose process, a chemical-intensive method similar to rayon production.
- Cellulose Extraction: Bamboo is crushed and soaked in a solution of sodium hydroxide and carbon disulfide, which breaks down the bamboo into a viscose solution.
- Spinning: The viscose solution is forced through spinnerets into a diluted sulfuric acid bath, which solidifies the fibers.
- Washing and Bleaching: The fibers are washed, bleached, and spun into yarn.
- Fabric Formation: The yarn is woven or knitted into soft, silky fabric.
While this process yields a luxurious fabric, it involves toxic chemicals that can pose environmental and health risks if not managed properly. Newer facilities are adopting closed-loop systems to recycle chemicals and reduce pollution.
Innovations in Bamboo Fabric Production: Lyocell and Nanotechnology
To address environmental concerns, manufacturers are increasingly using the lyocell process, which employs a non-toxic solvent (N-methyl morpholine-N-oxide) in a closed-loop system that recycles 99.5% of chemicals. This method produces high-quality bamboo lyocell fabric, combining sustainability and performance.
Additionally, nanotechnology is being explored to enhance bamboo fiber properties, improving durability and fabric functionality.
Why Bamboo Fabric Is Considered Sustainable.
Bamboo fabric's sustainability stems from several factors:
- Rapid Growth: Bamboo matures quickly without needing replanting.
- Low Water Usage: Bamboo requires significantly less water than cotton.
- Minimal Pesticides: Bamboo naturally resists pests, reducing chemical use.
- Carbon Sequestration: Bamboo absorbs more CO₂ and releases more oxygen than many trees.
- Biodegradability: Bamboo fabric decomposes naturally, unlike synthetic fibers.
When produced mechanically or via lyocell, bamboo fabric offers a truly eco-friendly alternative to conventional textiles.

Applications of Bamboo Fabric.
Bamboo fabric is utilized in:
Sustainable Clothing Fabric that is breathable and soft, ideal for casual wear or activewear as well as baby clothing.
"Home Textiles": Bed linens, towels, curtains, upholstery, and bedding.
"Luxury" Fashion The most expensive brands employ bamboo viscose as well as Lyocell blends to create luxurious, soft clothing.
Medical Textiles Antibacterial and hypoallergenic properties are ideal for products that are sensitive to skin.
Both cotton and bamboo have their own benefits so it really depends on what you need: comfort, durability, sustainability, budget.
Comfort: Bamboo is naturally soft and silky, like silk, and has great moisture wicking properties that keeps your skin dry and cool. Cotton is soft and breathable but can get rough over time unless it’s high quality like Egyptian or Pima cotton.
Durability: Cotton is more durable, can handle frequent washing and sunlight better than bamboo. Bamboo fabric is strong but can weaken with prolonged sunlight and chlorine exposure. But bamboo naturally resists odors and fungal growth.
Breathability and Moisture Management: Bamboo is breathable and moisture wicking, perfect for hot and humid climates or activewear. Cotton is breathable but less effective at moisture management than bamboo.
Sustainability: Bamboo is more sustainable because it grows fast without pesticides or fertilizers and uses way less water than cotton. Cotton farming uses a lot of water and pesticides which has a bigger environmental impact.
Care and Cost: Cotton is easier to care for and cheaper. Bamboo fabric is pricier but requires gentler washing to maintain its softness and shape.
Bamboo fabric is unique since it combines qualities made by nature and good environmental impact. This is what makes this place special:
No Smell
Bamboo isn’t treated with chemicals to stay odorless. Since its natural fibers don’t allow bacteria growth, your clothes are less likely to take on bad odors.
Free of probing allergy triggering chemicals, very gentle on your skin The fact that bamboo fibers are circular and smooth often makes them gentle for sensitive skin. People with allergies or eczema will find these especially beneficial.
This medicine is used to fight bacteria and fungi. There is a natural antimicrobial substance called bamboo kun that lasts in the stretchy bamboo fabric. Bacterial and fungal infections are stopped, so bamboo fabric is wholesome and safe to put on.
All Good Apparel’s products are breathable and dry fast. Bamboo fabric helps air reach your skin and removes moisture from it. Because bamboo fabric gets rid of sweat 40% better than cotton, you always enjoy being dry and comfortable in hot or humid conditions.
Eco-Friendly and Supporting
Sustainability Bamboo doesn’t depend on pesticides or a lot of water since it grows so quickly, so it’s replenishable. Unlike many conventional fabrics, bamboo fabric is biodegradable and not made with many chemicals.
UV Protection
Just like UPF clothing, bamboo fabric itself obstructs UV rays naturally. That’s why you’re less likely to develop sunburn or other skin issues. A touched hat feels soft and gentle. Since it’s so soft, almost as much as silk or cashmere, bamboo fabric suits any outfit you’d wear every day and your most luxurious items. Items Made to Last Because it is soft, bamboo fabric still has strong properties and does not lose its shape after multiple washes.
Climate Control Because of its ability to adjust to temperature, bamboo fabric helps you remain comfortable all year round.
Many people think bamboo fabric is just another word for rayon, as most products contain rayon (or viscose), yet they are not the same thing.
Rayon is created by turning natural cellulose from plants such as wood pulp or bamboo, into a fiber. The cellulose is dissolved with the help of chemicals and then regrown into fibers. People in the textile sector commonly refer to rayon and viscose as the same thing.
Any fabric that is produced from bamboo plants is called bamboo fabric. Bamboo that is chemically changed into rayon or viscose fibers is then called bamboo rayon or bamboo viscose. Therefore, bamboo fabric might be considered a rayon, since bamboo is used to make rayon, the final fiber.
It is also possible to create bamboo fabric (bamboo linen) using machines without chemicals and the result is more eco-friendly, but this isn’t widely used commercially.
Most bamboo fabric on the market is rayon, made from bamboo cellulose. Still, bamboo fabric is more than just rayon; its base is actual bamboo and rayon is the technique used to turn it into fabric
